Appearance
人工智能(ArtificialIntelligence)
运行环境:MacBook Pro M1Max 32G 1T
本文主要以PyTorch为主
资源链接
环境安装
Anaconda 下载地址
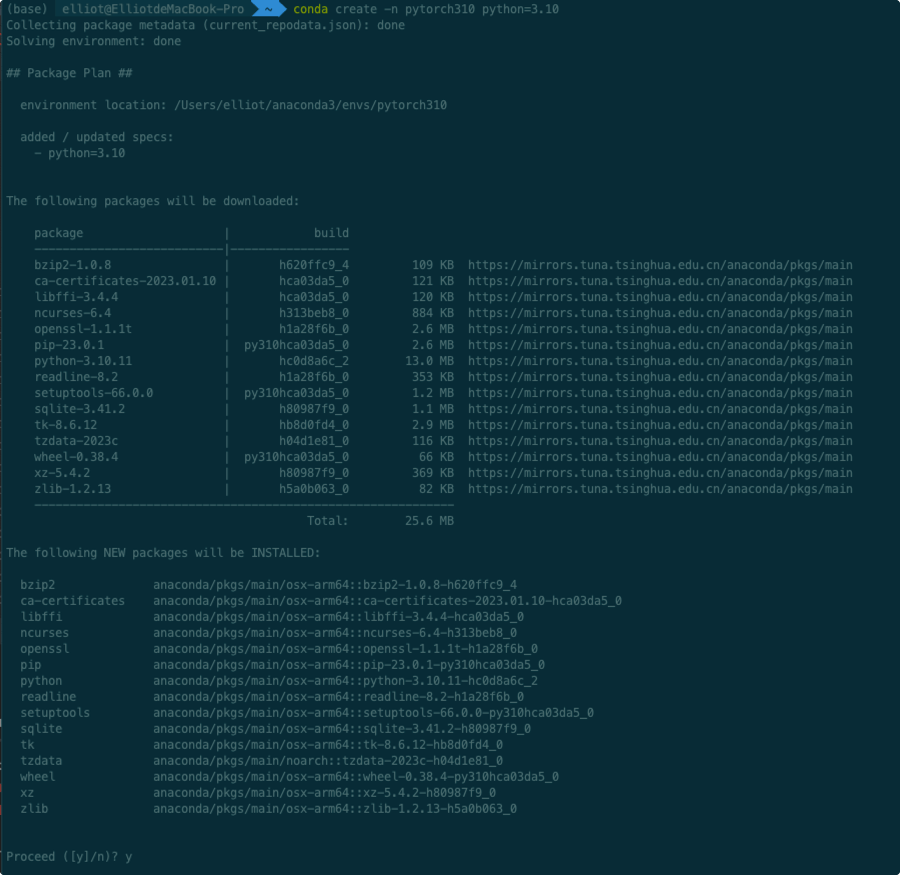
创建环境命令
conda create -n pytorch310 python=3.10
1
 激活环境命令
激活环境命令
conda activate pytorch310
1
 去激活环境命令
去激活环境命令
conda deactivate
1
报错处理:
1.移除代理
conda config --remove-key proxy12.使用镜像
conda config --set remote_read_timeout_secs 600 conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/free/ conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main/ conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/pytorch/1
2
33.临时禁用代理
conda config --set proxy_servers.http "" conda config --set proxy_servers.https ""1
2
Pytorch安装 官网地址
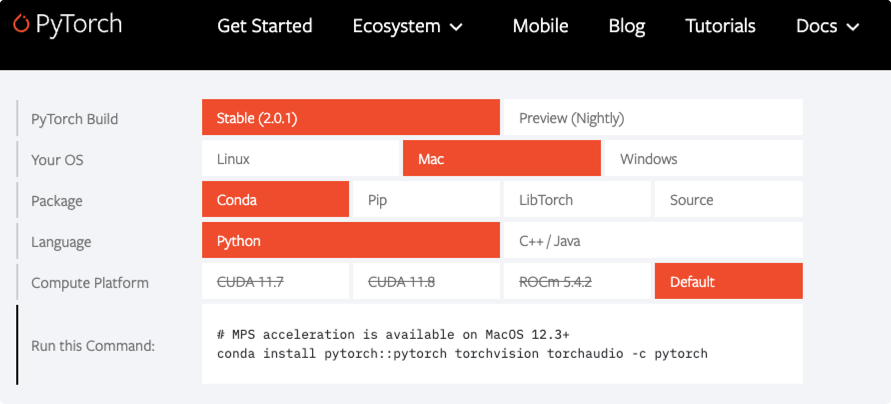 选择对应的版本,复制命令即可
选择对应的版本,复制命令即可
 省略其余安装包
省略其余安装包
 安装完成
安装完成
验证是否安装成功
pip 
命令行导入测试,无报错则安装成功 
!验证GPU加速
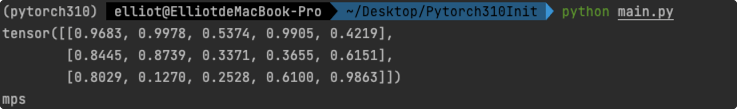
import torch
a = torch.rand(3,5)
print(a)
b = torch.device('mps')
print(b)
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
编辑器安装
Pycharm 下载地址
Jupiter 安装及使用
python < 3.10 以下可使用 conda install nb_conda
python >= 3.10 可使用 conda install -c conda-forge nb_conda_kernels
开启Jupyter NoteBook命令:jupyter notebook
激励函数 (Activation)
激励函数根据不同情况需要有不同选择
- 卷积神经网络:ReLU
- 循环神经网络:Relu Or Tanh
在AnaConda中使用matplotlib
conda install matplotlib
1
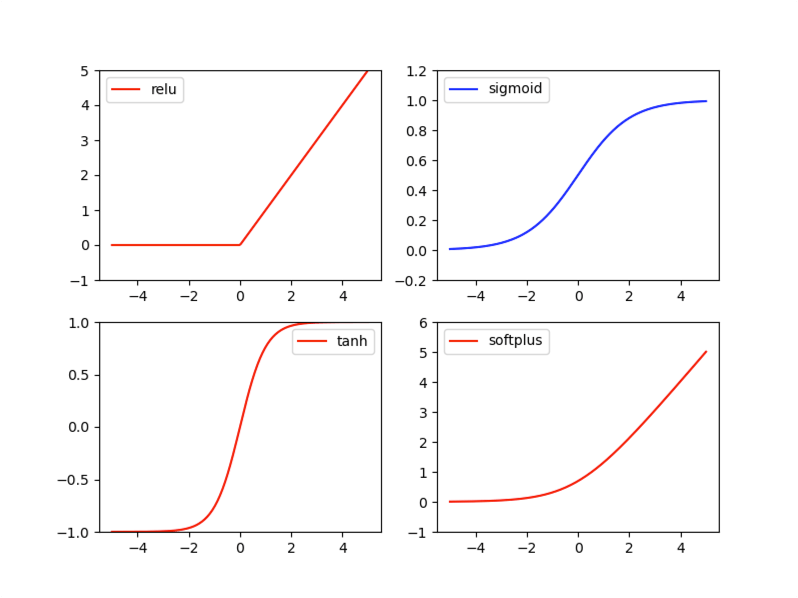
# 激励函数
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# fake data
# x data (tensor), shape=(100,1)
x = torch.linspace(-5, 5, 200)
x = Variable(x)
x_np = x.data.numpy()
y_relu = F.relu(x).data.numpy()
y_sigmoid = F.sigmoid(x).data.numpy()
y_tanh = F.tanh(x). data.numpy()
y_softplus = F.softplus(x).data.numpy()
plt.figure(1, figsize=(8, 6) )
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(x_np, y_relu, c='red', label='relu')
plt.ylim((-1, 5))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(x_np, y_sigmoid, c='blue', label='sigmoid')
plt.ylim((-0.2, 1.2))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(x_np, y_tanh, c='red', label='tanh')
plt.ylim((-1, 1))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(x_np, y_softplus, c='red', label='softplus')
plt.ylim((-1, 6))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
回归 Regression
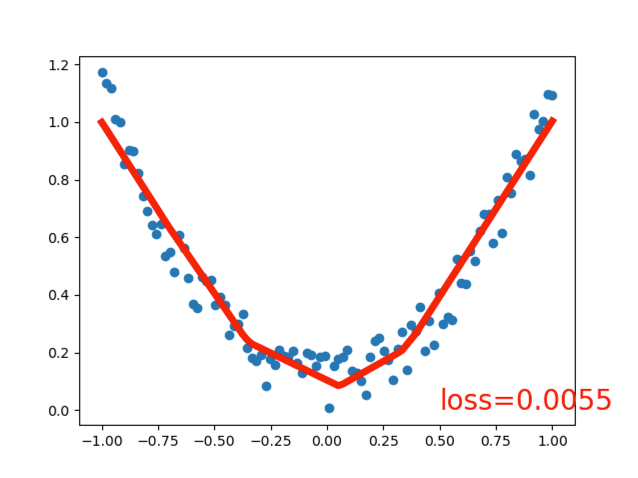
# 回归 Regression
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2 * torch.rand(x.size())
x, y = Variable(x), Variable(y)
# 打印
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
# plt.show()
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden)
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x))
x = self.predict(x)
return x
net = Net(1, 10, 1)
print(net)
plt.ion()
plt.show()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.5)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
for t in range(100):
prediction = net(x)
loss = loss_func(prediction, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if t % 5 == 0:
plt.cla()
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(0.5, 0, 'loss=%.4f' % loss.data.item(), fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
分类 Classification
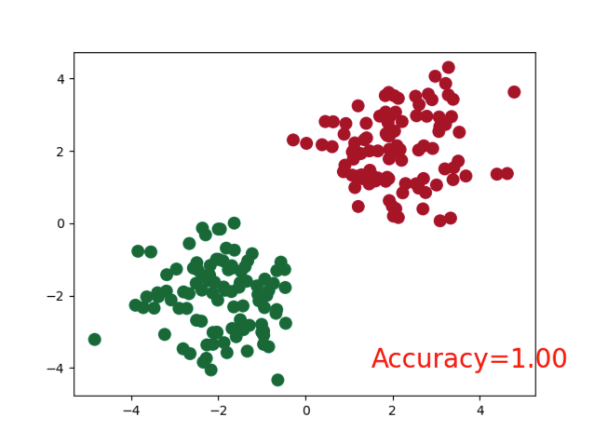
# 分类 Classification
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 不同的代码
n_data = torch.ones(100, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(2 * n_data, 1) # class0 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y0 = torch.zeros(100) # class0 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
x1 = torch.normal(-2 * n_data, 1) # class1 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y1 = torch.ones(100) # class2 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # FloatTensor = 32-bit floating
y = torch.cat((y0, y1), ).type(torch.LongTensor) # LongTensor = 64-bit integer
x, y = Variable(x), Variable(y)
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=y.data.numpy(), s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
plt.show()
# 打印
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
# plt.show()
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden)
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x))
x = self.predict(x)
return x
net = Net(2, 10, 2)
print(net)
plt.ion()
plt.show()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.02)
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
for t in range(100):
out = net(x)
loss = loss_func(out, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if t % 2 == 0:
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()
prediction = torch.max(F.softmax(out, dim=1), 1)[1] # 预测分类结果
pred_y = prediction.data.numpy()
target_y = y.data.numpy()
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=pred_y, s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
accuracy = float((pred_y == target_y).astype(int).sum()) / float(target_y.size)
plt.text(1.5, -4, 'Accuracy=%.2f' % accuracy, fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
快速搭建神经网络
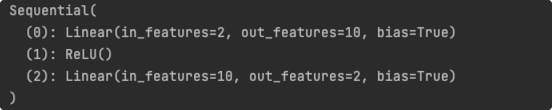
net2 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(2,10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10,2),
)
print(net2)
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
保存及提取
# 保存及提取神经网络
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# fake data
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1) # x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2*torch.rand(x.size()) # noisy y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
# The code below is deprecated in Pytorch 0.4. Now, autograd directly supports tensors
# x, y = Variable(x, requires_grad=False), Variable(y, requires_grad=False)
def save():
# save net1
net1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net1.parameters(), lr=0.5)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
for t in range(100):
prediction = net1(x)
loss = loss_func(prediction, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# plot result
plt.figure(1, figsize=(10, 3))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.title('Net1')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
# 2 ways to save the net
torch.save(net1, '04net.pkl') # save entire net
torch.save(net1.state_dict(), '04net_params.pkl') # save only the parameters
def restore_net():
# restore entire net1 to net2
net2 = torch.load('04net.pkl')
prediction = net2(x)
# plot result
plt.subplot(132)
plt.title('Net2')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
def restore_params():
# restore only the parameters in net1 to net3
net3 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
# copy net1's parameters into net3
net3.load_state_dict(torch.load('04net_params.pkl'))
prediction = net3(x)
# plot result
plt.subplot(133)
plt.title('Net3')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.show()
# save net1
save()
# restore entire net (may slow)
restore_net()
# restore only the net parameters
restore_params()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
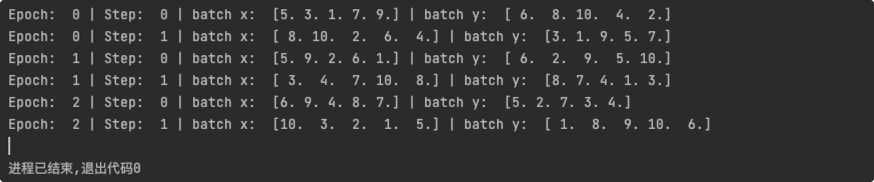
分批训练
# 分批训练
import torch
import torch.utils.data as Data
torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
BATCH_SIZE = 5
# BATCH_SIZE = 8
x = torch.linspace(1, 10, 10) # this is x data (torch tensor)
y = torch.linspace(10, 1, 10) # this is y data (torch tensor)
torch_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x, y)
loader = Data.DataLoader(
dataset=torch_dataset, # torch TensorDataset format
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, # mini batch size
shuffle=True, # random shuffle for training
num_workers=2, # subprocesses for loading data
)
def show_batch():
for epoch in range(3): # train entire dataset 3 times
for step, (batch_x, batch_y) in enumerate(loader): # for each training step
# train your data...
print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| Step: ', step, '| batch x: ',
batch_x.numpy(), '| batch y: ', batch_y.numpy())
if __name__ == '__main__':
show_batch()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
